For factories and manufacturers, the First Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century was a turning point. After that, companies and production lines began combining the efforts of humans with mechanical ones. Manufacturers have changed with the times, taking advantage of new ways to make things as they become available to increase output, improve efficiency, and lower worker risks.
In today’s era of cutting-edge computing, artificial intelligence, and other innovations, factories everywhere are eager to adopt the next great thing in productive efficiency. Here come cobots or collaborative robots. Discover the benefits of using collaborative robots in your manufacturing processes.
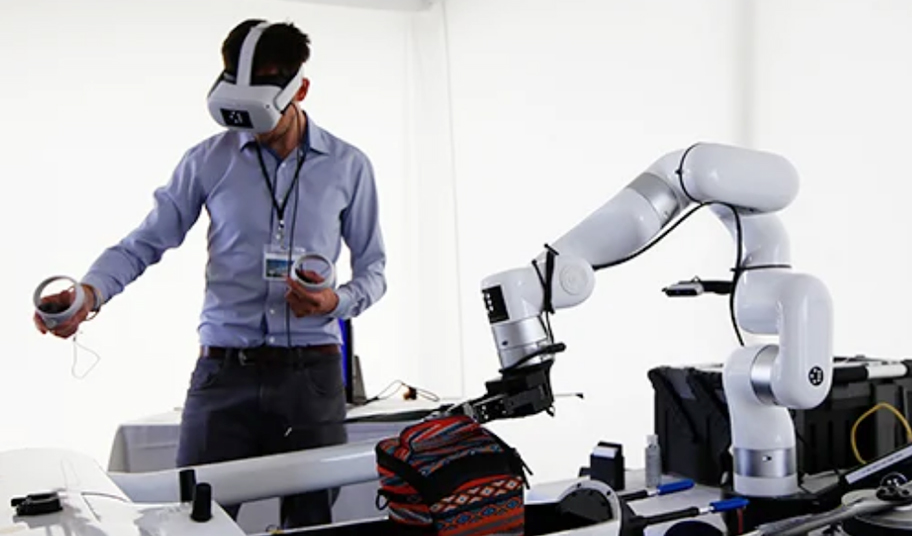
A collaborative robot is designed to work alongside humans. There are already machines in manufacturing that need humans to operate, but a collaborative robot is different in such a way that it interacts and works alongside humans in the same step of their production.
History of cobot
Cobots were made in 1996 because of a project that started two years before. In 1994, General Motors Robotics Center’s Prasad Akella wanted to find a way for robots and people to work together safely. In 1995, he got a research grant from the General Motors Foundation to do this. The first collaborative robot was then made by J. Edward Colgate and Michael Peshkin, two professors at Northwestern University. A year later, in 1997, they got a patent for it.
Colgate and Peshkin went on to start their own company, Cobotics, where they made the first cobots that were used in manufacturing. They were used in the final assembly line of car companies. In 2003, Stanley Assembly Technologies bought the company. Since then, different kinds of collaborative robots have been developed by other companies to meet the needs of different industries.
In 2004, KUKA introduced the world to the LBR 3 cobot. Then later, with the KUKA LBR 4 in 2008 and the KUKA LBR iiwa in 2013, KUKA further developed the technology.
In 2008, Universal Robots shocked the world with the UR5. The UR10 cobot came out in 2012, followed by the UR3 in 2015, which is smaller and has a lighter payload.
Baxter, an industrial cobot from Rethink Robotics, debuted in 2012, and Sawyer, a smaller, faster collaborative robot built for high-precision jobs, was unveiled in 2015.
In 2015, FANUC unveiled the FANUC CR-35iA, a collaborative robot that could lift up to 35 kilograms. FANUC has since created a more limited series of collaborative robots. But it wasn’t until 2015 that ABB unveiled YuMi, the world’s first collaborative dual-arm robot. Cobots were very expensive until UFactory came to take over with cheaper prices.
UFactory released xArm5, xArm6, and xArm7 (the world first cobot under$10,000) in 2018. It breaks the barrier of cobot pricing by making cobots more affordable for all types of companies. UFactory launchs a new cobot—UFACTORY 850 in 2023, it’s a truely industrial collaborative robot with a 50% faster accelteration, a 20% longest reach, a more precise repeatability, 50% thickest materials, and a 70% heaviest payload.
Recently, the market for industrial cobots has grown at a 50% annual rate, and there are signs of more growth.
What is human-robot collaborative specified as?
In human-robot collaboration, the collaborative robot(cobot) provides assistance to the human operator. This means that the machine doesn’t replace the person. Instead, it improves the person’s abilities and frees him from heavy responsibilities. These can include activities such as working at heights or moving heavy weights.
Why do we need human-robot collaboration?
Human Collaborative Robots, through the use of mobile platforms, can be made mobile and given the ability to execute a variety of activities in a flexible manner. They are, therefore, able to be deployed individually at any location and for any function that matches production requirements. For instance, the needed batch size may determine which location they are installed at. Furthermore, these robots offer maximum flexibility by way of spontaneous automation.
How can humans and robots work together?
The majority of people in today’s world view robots and other forms of artificial intelligence as slaves who perform tasks in the background, or they could be machines that have replaced humans in repetitive jobs such as those held by bank tellers and workers on assembly lines.
But technology is getting better and better to the point where machines may soon be able to work with people as equals.Researchers and private companies are looking into a wide range of ways to improve how robots and systems with artificial intelligence work with people.
Here are some of the ways it can be done:
The kinds of labor that people don’t like to undertake, such as carrying heavy objects, testing chemicals, and calculating data, are the kinds of work that should be delegated to robots. So, people are free to focus on the things they are good at, such as responding well to changing situations and coming up with new ways to solve problems.
How do humans and robots collaborate to achieve a goal?
While some academics have suggested that robots and humans can’t establish shared experiences and knowledge, other researchers are working hard to devise strategies to make this possible. Machine learning is expected to help robots learn what to expect from their human coworkers. When combined with human intelligence, both parties will get an understanding of the abilities, limitations, and modes of behavior of the other.
Benefits of collaborative robots
1. Higher profit and employment rate
The notion that robots are replacing humans is false. Robots won’t replace humans; conversely, they will help firms make more profits, and then firms will need more workers. To back this up, between 1978 and 2017, Daisuke Adachi of Yale University and his colleagues looked into the manufacturing industry in Japan. They came to the conclusion that firms hired 2.2% more people when they added one robot unit for every thousand workers.
Also, Joonas Tuhkuri and his colleagues at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology did a study on Finnish companies. They found that when these companies started using more modern technologies, they hired more people. Michael Webb of Stanford University and Daniel Chandler of the London School of Economics did research on machine tools in British industry that hasn’t been published yet. They found that automation had “a strong positive relationship with firm survival” and that more automation at the start was linked to more jobs.
2. Shortage of workers
Despite a worldwide increase in investment over the past two years, there is still little proof that automation will cause job losses. It’s hard to square the reality of a record 30 million unfilled openings throughout the OECD with the notion that humans are obsolete in today’s prosperous economies. As a whole, low-skilled jobs are assumed to be more at risk of being automated away, but this doesn’t explain the rapid wage rise in this sector. Even though “routine” jobs are thought to be simpler to automate, there is little evidence to suggest that they are disappearing in the United States.
3. Saving cost and Increasing ROI
Thanks to improvements in collaborative technology over the past few years, investing in cobots can often give a positive return on investment (ROI) in less than a year. These robots can be put in the same place as people, which means they can work with them. This cuts out extra steps and saves time. Many clients find appeal in the interesting, cutting-edge technology that Cobots bring in. At the same time, increasing productivity and lowering labor costs means you’re saving more money.
4. Effective production withshorter cycle times
Cobots can do some jobs more reliably and consistently than humans can. They can also be changed to work in many different places and can be moved and used quickly and easily. Users of cobots will find that they are able to accomplish more because of these features.
Cobots can work around the clock, which helps reduce cycle times and facilitates just-in-time production.
5.Unlimited Possibilities
For collaborative robots, this is just the beginning. Exactly how humans will be utilized in the future of highly automated manufacturing applications is uncertain. Collaborative robots currently account for 5% of the robot market. The availability of cobots among manufacturers and engineers will lead to a rapid rise in this industry. Once they do that, they can begin to explore their options in any field, from the medical device sector to the packaging industry and everything in between.
Collaborative robot V.S. Industrial robot
1. Pricing
About 50% of the money is saved using collaborative robots, while on the other hand, industrial robots are quite expensive.
2. Safety
The safety of workers is very important, and industrial robots are the culprit to that. With their isolation from safety cages, workers are easily injured. This is not the same with collaborative robots, as they are made to work hand in hand with humans at low speed. Default collision detection and external sensors are also in place in cobot in case of emergencies.
3. Flexibility
One of the major differences between a cobot and an industrial robot is its ability to be moved in different areas and do diverse work, whereas industrial robots’ production lines are mostly fixed and hard to change.
4. Programming
With the use of C++, Python, and ROS, coding robots is now easy. Cobots are beginner friendly and have a high-teaching function, unlike Industrial robots that need a certified programmer to make them work and are also difficult to repurpose and reprogram for a different field.
5. Deployment
Need an easy, fast setup? Cobot offers it with less stress; with its plug-and-play function, it is ready to work. Unlike Industrial robots that require that money is spent on professionals to operate them, time is also spent on learning the specific functionality it has.
6. Performance
Cobots have a lesser payload than Industrial robots, with a -20kg and a shorter reach of -1700mm, cobots work at a low to medium speed. Compared to an industrial robot that does the heavy lifting with its higher speed and longer reach of 4000mm.
7. Weight
Industrial robots are known for their heavy weight, making it difficult to be moved around, but collaborative robots come in a lighter version making everything easy.
8. Capability
Because of their speed and payload, Industrial robots are used in large industries for performing heavy tasks, but cobots, on the other hand, are environmentally friendly and are used commercially in restaurants, stores, etc., to perform light tasks.
9. Taking up space
Cobots make use of smaller workspaces compared to industrial robots, which take more than twice the cobots’ space.
10. Size
A compact size and a better appearance make cobots well suited for the commercial world, but that’s not the case with Industrial robots, which are very large, and less focus is directed to their appearance but their functionality.
SUMMARY
As Baby Boomers age, the labor pool shrinks, and the cost of doing business rises. In response, businesses are increasingly turning to innovative technology to remain competitive. Companies like UFactory that produce cobots aim to address these manpower and cost issues. As the current era of humans working with robotic colleagues is becoming the standard for improved performance, interest in cobots is only expected to continue.
References
https://www.tm-robot.com/en/what-does-collaborative-robot-mean/
https://www.wevolver.com/article/humanrobot.collaboration.3.case.studies
https://theconversation.com/5-ways-to-help-robots-work-together-with-people-101419
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cobot
https://sp-automation.co.uk/benefits-of-working-with-collaborative-robots/